前言
java猿在面试中,经常会被问到1个问题:
java实现同步有哪几种方式?
大家一般都会回答使用synchronized, 那么还有其他方式吗? 答案是肯定的, 另外一种方式也就是本文要说的ThreadLocal。
ThreadLocal介绍
ThreadLocal, 看名字也能猜到, “线程本地”, “线程本地变量”。 我们看下官方的一段话:
This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its get or set method) has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable. ThreadLocal instances are typically private static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., a user ID or Transaction ID).
粗略地翻译一下:
ThreadLocal这个类提供线程本地的变量。这些变量与一般正常的变量不同,它们在每个线程中都是独立的。ThreadLocal实例最典型的运用就是在类的私有静态变量中定义,并与线程关联。
什么意思呢? 下面我们通过1个实例来说明一下:
jdk中的SimpleDateFormat类不是一个线程安全的类,在多线程中使用会出现问题,我们会通过线程同步来处理:
使用synchronized
private static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); public synchronized static String formatDate(Date date) { return sdf.format(date); }使用ThreadLocal
private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> formatter = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>(){ @Override protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() { return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); } }; public String formatIt(Date date) { return formatter.get().format(date); }
这两种方式是一样的,只不过一种用了synchronized,另外一种用了ThreadLocal。
synchronized和ThreadLocal的区别
使用synchronized的话,表示当前只有1个线程才能访问方法,其他线程都会被阻塞。当访问的线程也阻塞的时候,其他所有访问该方法的线程全部都会阻塞,这个方法相当地 “耗时”。
使用ThreadLocal的话,表示每个线程的本地变量中都有SimpleDateFormat这个实例的引用,也就是各个线程之间完全没有关系,也就不存在同步问题了。
综合来说:使用synchronized是一种 “以时间换空间”的概念, 而使用ThreadLocal则是 “以空间换时间”的概念。
ThreadLocal原理分析
我们先看下ThreadLocal的类结构:
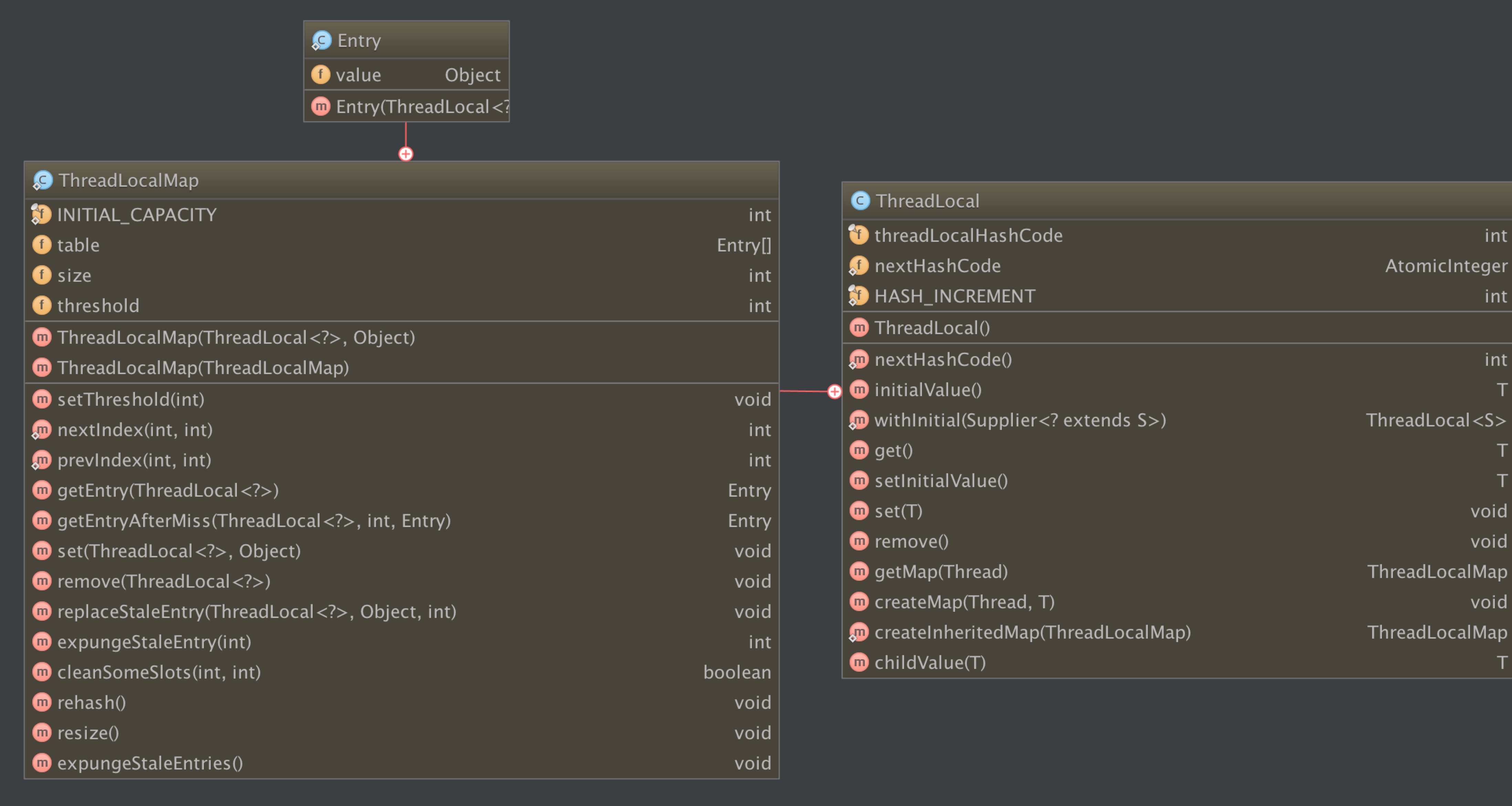
我们看到ThreadLocal内部有个ThreadLocalMap内部类,ThreadLocalMap内部有个Entry内部类。
先介绍一下ThreadLocalMap和ThreadLocalMap.Entry内部类:
ThreadLocalMap其实也就是一个为ThreadLocal服务的自定义的hashmap类。
Entry是一个继承WeakReference类的类,也就是ThreadLocalMap这个hash map中的每一项,并且Entry中的key基本上都是ThreadLocal。
再下来我们看下Thread线程类:
Thread线程类内部有个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的属性:
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
下面重点来看ThreadLocal类的源码:
public T get() {
// 得到当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 拿到当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
// 找到该ThreadLocal对应的Entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
// 当前线程没有ThreadLocalMap对象的话,那么就初始化ThreadLocalMap
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
// 初始化ThreadLocalMap,默认返回null,可由子类扩展
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
// 实例化ThreadLocalMap之后,将初始值丢入到Map中
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
public void set(T value) {
// set逻辑:找到当前线程的ThreadLocalMap,找到的话,设置对应的值,否则创建ThreadLocalMap
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
注释已经写了,读者有不明白的可以自己看看源码。
ThreadLocal的应用
ThreadLocal应用广泛,下面介绍下在SpringMVC中的应用。
RequestContextHolder内部结构
RequestContextHolder:该类会暴露与线程绑定的RequestAttributes对象,什么意思呢? 就是说web请求过来的数据可以跟线程绑定, 用户A,用户B分别请求过来,可以使用RequestContextHolder得到各个请求的数据。
RequestContextHolder数据结构: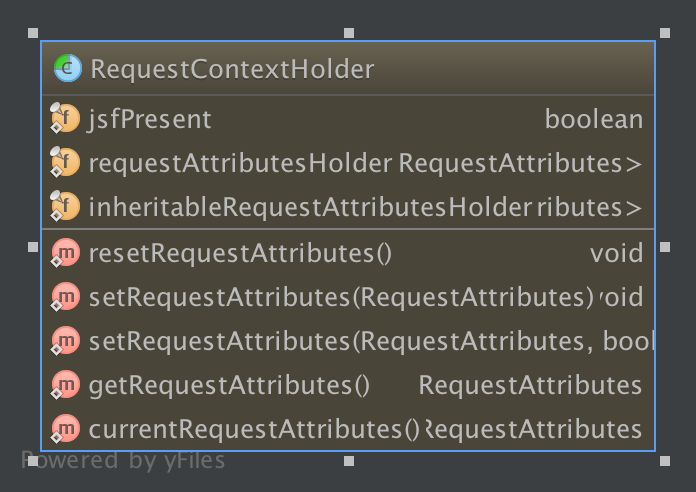
具体这两个holder:
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request context");
这里的NamedThreadLocal只是1个带name属性的ThreadLocal:
public class NamedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
private final String name;
public NamedThreadLocal(String name) {
Assert.hasText(name, "Name must not be empty");
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.name;
}
}
继续看下RequestContextHolder的getRequestAttributes方法,其中接口RequestAttributes是对请求request的封装:
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
// 直接从ThreadLocalContext拿当前线程的RequestAttributes
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
我们看到,这里直接使用了ThreadLocal的get方法得到了RequestAttributes。
当需要得到Request的时候执行:
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = requestAttributes.getRequest();
RequestContextHolder的初始化
以下代码在FrameworkServlet代码中:
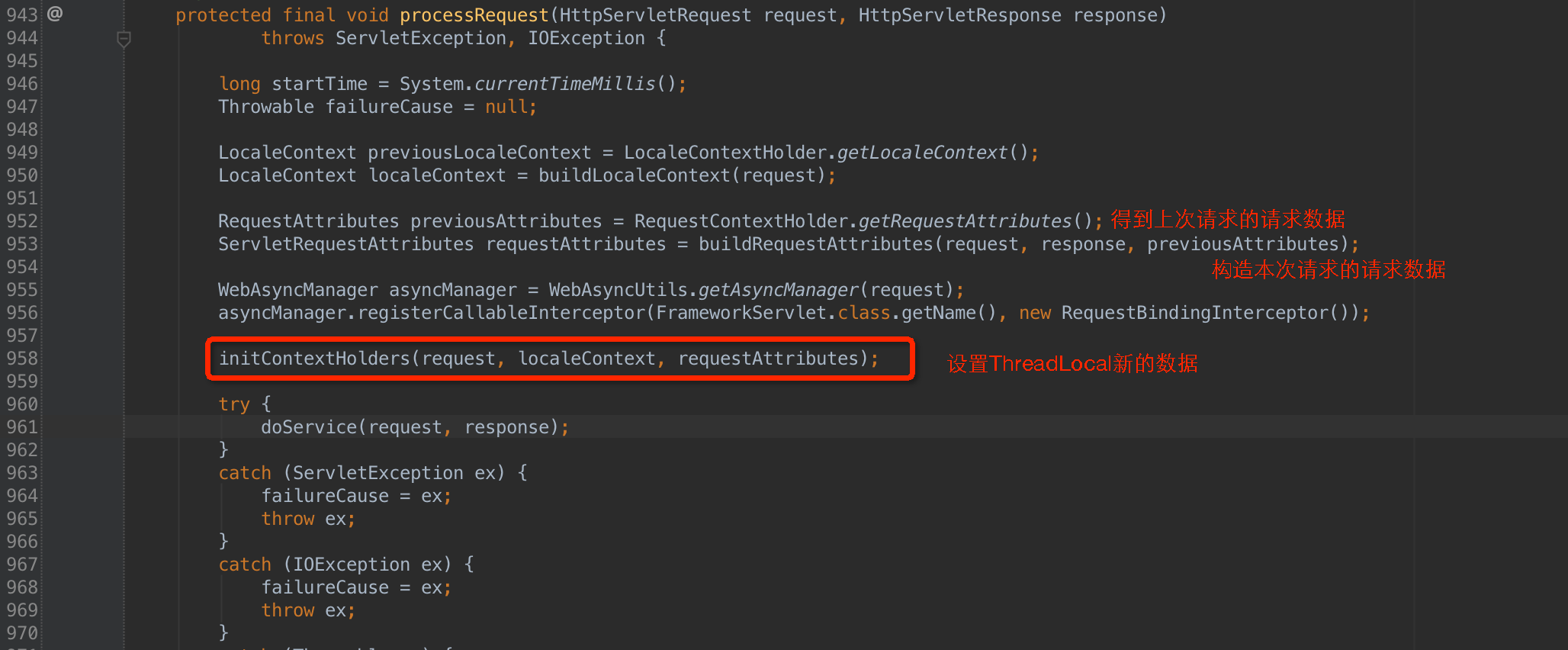
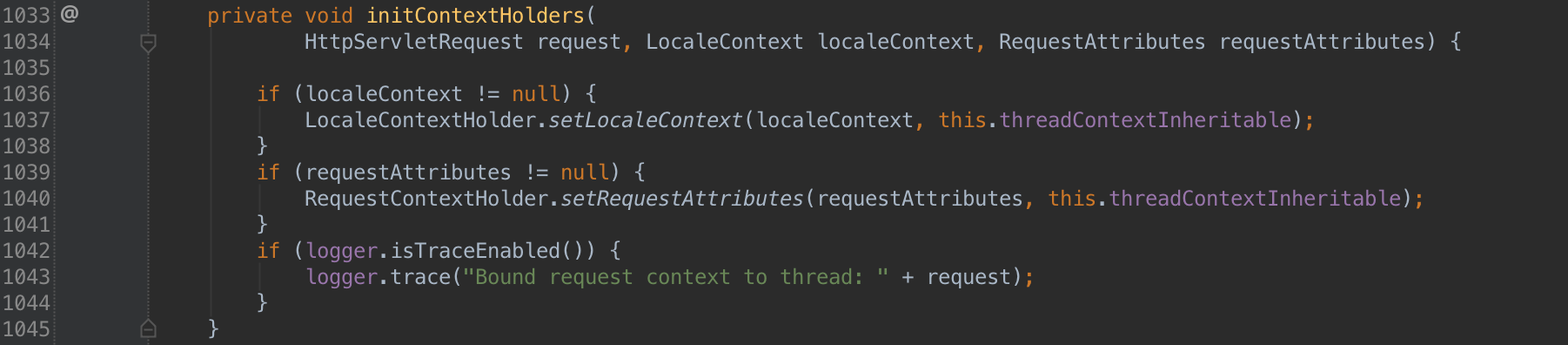
总结
本文介绍了ThreadLocal的原理以及ThreadLocal在SpringMVC中的应用。个人感觉ThreadLocal应用场景更多是共享一个变量,但是该变量又不是线程安全的,而不是线程同步。比如RequestContextHolder、LocaleContextHolder、SimpleDateFormat等的共享应用。
